Statistics Programs
Sample data
Have these files ready beforehand to run the following sample programs.
ex1.txt
data1.txt
data2.txt
data3.txt
data4.txt
Right click to save these.
(These are generated by using random numbers.)
Descriptive Statistics
Read a file to calculate the number of items, the mean and the standard deviation.
100 OPEN #1: NAME "ex1.txt"
110 LET n=0 ! Number of items
120 LET s=0 ! Sum
130 LET s2=0 ! Sum of Square
140 DO
150 INPUT #1,IF MISSING THEN EXIT DO : x
160 LET n=n+1
170 LET s=s+x
180 LET s2=s2+x^2
190 LOOP
200 PRINT "Number of items",n
210 PRINT "Mean",s/n
220 PRINT "Standard deviation",SQR(s2/n-(s/n)^2)
230 CLOSE #1
240 END
|
Make a distribution table from a test result of full mark 10 point.
120 DIM f(0 TO 10)
130 MAT f=ZER
140 OPEN #1: NAME "data2.txt"
150 DO
160 INPUT #1,IF MISSING THEN EXIT DO : x
170 LET f(x)=f(x)+1
180 LOOP
190 CLOSE #1
200 FOR x=0 TO 10
210 PRINT x;"point", f(x);"persons"
220 NEXT x
230 END
|
Make a class width 10 distribution table of a test result with full mark 100 point.
110 DIM f(0 TO 10)
120 MAT f=ZER
130 OPEN #1: NAME "data3.txt"
140 DO
150 INPUT #1,IF MISSING THEN EXIT DO : x
160 LET i=INT(x/10)
170 LET f(i)=f(i)+1
180 LOOP
190 CLOSE #1
200 FOR i=0 TO 10
210 PRINT i*10;"s point",f(i);"persons"
220 NEXT i
230 END
|
Read bivariate data to sum up the means, the standard deviations and the correlation.
100 OPEN #1:NAME "data4.txt"
110 LET n=0 ! number of items
120 LET mx=0 ! sum of x
130 LET my=0 ! sum of y
140 LET xx=0 ! sum of x^2
150 LET yy=0 ! sum of y^2
160 LET xy=0 ! sum of x*y
170 DO
180 INPUT #1,IF MISSING THEN EXIT DO:x,y
190 LET n=n+1
200 LET mx=mx+x
210 LET my=my+y
220 LET xx=xx+x^2
230 LET yy=yy+y^2
240 LET xy=xy+x*y
250 LOOP
260 LET mx=mx/n ! mean of x
270 LET my=my/n ! mean of y
280 LET sx=SQR(xx/n-mx^2) ! sd of x
290 LET sy=SQR(yy/n-my^2) ! sd of y
300 LET sxy=xy/n-mx*my
310 PRINT sxy/(sx*sy) ! correlation
320 CLOSE #1
330 END
|
PLot a scatter graph
110 OPEN #1:NAME "data4.txt"
120 SET WINDOW 100,200,0,100
130 DRAW grid WITH SCALE(10,10)
140 DO
150 INPUT #1,IF MISSING THEN EXIT DO: x,y
160 PLOT POINTS:x,y
170 LOOP
180 CLOSE #1
190 END
|
Plot two regression lines.
100 OPEN #1:NAME "data4.txt"
110 ! preparation
120 LET n=0 ! Number of Items
130 LET mx=0 ! Sum of x
140 LET my=0 ! Sum of y
150 LET xx=0 ! Sum of x^2
160 LET yy=0 ! Sum of y^2
170 LET xy=0 ! Sum of x*y
180 ! Coordinate setting
190 LET left=100
200 LET right=200
210 LET bottom=0
220 LET top=100
230 SET WINDOW left,right,bottom,top
240 DRAW grid WITH SCALE(10,10)
250 ! Read data
260 DO
270 INPUT #1,IF MISSING THEN EXIT DO: x,y
280 LET n=n+1
290 LET mx=mx+x
300 LET my=my+y
310 LET xx=xx+x^2
320 LET yy=yy+y^2
330 LET xy=xy+x*y
340 PLOT POINTS:x,y
350 LOOP
360 ! make a suumury
370 LET mx=mx/n ! mean of x
380 LET my=my/n ! mean of y
390 LET sx=SQR(xx/n-mx^2) ! sd of x
400 LET sy=SQR(yy/n-my^2) ! sd of y
410 LET sxy=xy/n-mx*my
420 LET r=sxy/(sx*sy) ! correlation
430 ! draw regression lines
440 DEF f(x)=a*(x-mx)+my
450 SET LINE STYLE 2
460 LET a=r*sy/sx
470 PLOT LINES:left,f(left);right,f(right)
480 SET LINE STYLE 3
490 LET a=1/r*sy/sx
500 PLOT LINES:left,f(left);right,f(right)
510
520 CLOSE #1
530 END
|
Probabilities
Probability distribution of the number of dice with spot 1 rolling n dice.
110 OPTION ARITHMETIC NATIVE
120 SET WINDOW -1,49,-0.01,0.49
130 DRAW axes0
140 INPUT n
150 FOR k=0 TO n
160 LET p=Comb(n,k)/6^n*5^(n-k)
170 PLOT LINES: k-0.5,0 ; k-0.5,p ; k+0.5,p ; k+0.5,0
180 NEXT k
190 END
|
A simulation of a distribution of sample means.
100 DIM a(1000) ! population
110 LET n=10 ! sample size
120 DIM s(n) ! sample
130 OPEN #1: NAME "data3.txt"
140 FOR i=1 TO 1000
150 INPUT #1:a(i)
160 NEXT i
170 CLOSE #1
180 DIM d(0 TO 100)
190 MAT d=ZER
200 RANDOMIZE
210 LET times=2000 ! number of experiment
220 FOR t=1 TO times
230 FOR i=1 TO n
240 LET s(i)=a(INT(RND*1000)+1)
250 NEXT i
260 LET m=0
270 FOR i=1 TO n
280 LET m=m+s(i)
290 NEXT i
300 LET m=m/n
310 LET i=INT(m)
320 LET d(i)=d(i)+1
330 NEXT t
340 SET WINDOW 0,100,0,0.4
350 FOR i=0 TO 100
360 PLOT AREA:i,0;i+1,0;i+1,d(i)/times;i,d(i)/times
370 NEXT i
380 END
|
Distributions of the averages of k dice and the normal distributions approximating them.
100 DIM f(10,60)
110 MAT f=ZER
120 FOR x=1 TO 6
130 LET f(1,x)=1
140 NEXT x
150 FOR k=2 TO 10
160 FOR x=k TO 6*k
170 FOR y=x-6 TO x-1
180 IF k-1<=y AND y<=6*(k-1) THEN LET f(k,x)=f(k,x)+f(k-1,y)
190 NEXT y
200 NEXT x
210 NEXT k
220 SET WINDOW -1, 7, -0.03, 1
230 FOR k=1 TO 10
240 CLEAR
250 SET LINE COLOR 1
260 DRAW axes
270 LET w=1/k
280 FOR x=k TO 6*k
290 LET h=f(k,x)/6^k/w
300 PLOT LINES: x/k-w/2,0; x/k-w/2,h; x/k+w/2,h; x/k+w/2,0
310 NEXT x
320 WAIT DELAY 1
330 LET m=7/2
340 LET s2=35/12/k
350 LET s=SQR(s2)
360 SET LINE COLOR 4
370 FOR x=0 TO 7 STEP 0.01
380 PLOT LINES:x,1/(SQR(2*PI)*s)*EXP(-(x-m)^2/(2*s2));
390 NEXT x
400 PLOT LINES
410 WAIT DELAY 1
420 NEXT k
430 END
|
Cumulative distribution of a binomial distribution B(n, p).
100 OPTION ARITHMETIC NATIVE
110 DECLARE EXTERNAL FUNCTION C
120 LET n=180
130 LET p=1/6
140 LET t=0
150 FOR k=0 TO n
160 LET t=t+C(n,k)*p^k*(1-p)^(n-k)
170 PRINT USING "### #.######":k,t
180 NEXT k
190 END
200 ! the binomial coefficient
210 EXTERNAL FUNCTION C(n,r)
220 OPTION ARITHMETIC NATIVE
230 IF r=0 THEN LET C=1 ELSE LET C=C(n-1,r-1)*n/r
240 END FUNCTION
|
This program can be applied for at most n=1020. If n exceeds 1020, an overflow will occur in calculation of the binomial coefficient.
Cumulative distribution of a binomial distribution B(n, p), revised.
100 OPTION ARITHMETIC NATIVE
110 LET n=1200
120 LET p=1/6
130 LET t = (1-p)^n ! Cumulative probability
140 LET u = 0 ! Logarithm of the binomial coefficient
150 FOR k = 1 TO n
160 LET u = u + LOG2(n-k+1)-LOG2(k)
170 LET t = t + 2^( u + k*LOG2(p) + (n-k)*LOG2(1-p))
180 PRINT USING "##### #.######":k,t
190 NEXT k
200 END
|
Overflow is suppressed using logarithm.
More sample programs are put to the public
here (in Japanese).
Statistics Library
Several libraries are included in the Library folder of Decimal BASIC.
You can load and check the contents by selecting "Library" as the "File Type" in the "Open File" menu of BASIC and then selecting the Library folder.
STAT1.lib contains external subprograms that target one-dimensional arrays.
STAT2.lib contains external subprograms that target two-dimensional arrays.
When using a library, add a MERGE statement specifying the library file name to the end of the program. When
you write a MERGE statement, the specified library is added to the program and compiled.
STAT1.lib
STAT1.lib has following external functions:
mean (a()) mean of 1-dim array a.
variance(a()) variance of 1-dim array a.
sd(a()) standard devation of 1-dim array a.
mini(a()) the minimum value in 1-dim array a.
maxi(a()) the maximum value in 1-dim array a.
STAT1.lib has an external subprogram histgram(a(), mi, ma, w)
Example 1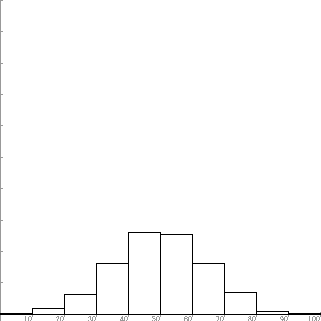
100 DIM a(1000)
110 OPEN #1:NAME "data3.txt"
120 LET n=1
130 DO
140 INPUT #1, IF MISSING THEN EXIT DO: a(n)
150 LET n=n+1
160 LOOP
170 CLOSE #1
180 LET n=n-1
190 MAT REDIM a(n)
200 CALL histogram(a,0,100,10)
210 END
220 MERGE "STAT1.lib"
The external subprogram histogram(a(),mi,ma,w) defined in STAT1.lib examines the distribution of the values recorded in the one-dimensional array a and displays it as a histogram.
The second and third arguments specify the range of values, and the fourth argument specifies the width of the classes.
A large array is prepared in advance for reading the data, and its size is adjusted when it is passed to the external subprogram histogram.
The value of n when exiting the DO-LOOP in lines 130-160 is the value when INPUT #1 in line 140 fails, so the size of the array to be redefined is reduced by one as shown in line 180.
The MAT REDIM statement in line 190 resets the size of the array.
STAT2.lib
STAT2.lib has following functions, where x(,) is a 2-dim array, i.e. a matrix.
mean(x(,), n) mean of n-th column.
covariance (x(,), i, j) covariance between i-th and j-th columns.
variance(x(,), n) variance of n-th column.
sd(x(,),n) standard deviation of n-th column.
correlation(x(,), i, j) correlation between i-th and j-th columns.
STAT2.lib has two external subprograms:
scatter(x(,), i, j) plot the scatter graph between i-th and j-th columns.
chart(x(,), i ,j) plot the scatter graph and the regression line between i-th and j-th columns.
Example 2 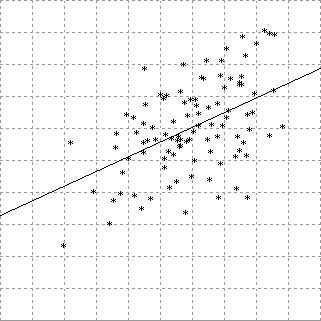
100 DIM a(1000,2)
110 OPEN #1:NAME "data4.txt"
120 LET n=1
130 DO
140 INPUT #1, IF MISSING THEN EXIT DO: a(n,1),a(n,2)
150 LET n=n+1
160 LOOP
170 CLOSE #1
180 LET n=n-1
190 MAT REDIM a(n,2)
200 SET WINDOW 100,200,0,100
210 DRAW GRID(10,10)
220 CALL chart(a,1,2)
230 END
240 MERGE "STAT2.lib"
The external subprogram chart(x(,),i,j) defined in STAT2.lib draws a correlation diagram and regression line between the i-th and j-th columns of the two-dimensional array x.
The coordinate system is set by the caller (see line 200).
As in Example 1, the size of the array passed to the external subprogram chart is adjusted in advance.
Decimal BASIC has a library of calculating some probability distributions.
PROBDIST.LIB has normal, t, χ2 (Chi-square),F distributions,
DiscDist.LIB has binomial, hyper-geometric, Poisson, negative binomial distributions.
These files are located in the subfolder "Library".
See Probability and Statistics Library for detail.
Example of usage.
Cumulative distribution Pr(X ≤ i), where X is the number of inferior goods sampling 6 without replacement from the bulk of 18000 goods which contains 3000 inferior goods.
10 DECLARE EXTERNAL FUNCTION HyperGeomLCum
20 DECLARE NUMERIC NN,M,n,i
30 LET NN=18000
40 LET M=3000
50 LET n=6
60 FOR i=0 TO n
70 PRINT i,HyperGeomLCum(NN,M,n,i)
80 NEXT i
90 END
100 MERGE "discdist.LIB"
Back